
When selecting an electric linear actuator, understanding how torque, force, and speed work together is key to achieving the right balance of performance and efficiency. Each factor influences the others, and trade-offs between them determine how well an actuator fits your application.
In this article, we’ll explain what these three parameters mean, how they interact, and how to use that knowledge to choose the right electric linear actuator for your application.
Looking for a fast way to get started? Explore our electric linear actuators to compare models and specifications.
What Do Torque, Force, and Speed Mean?
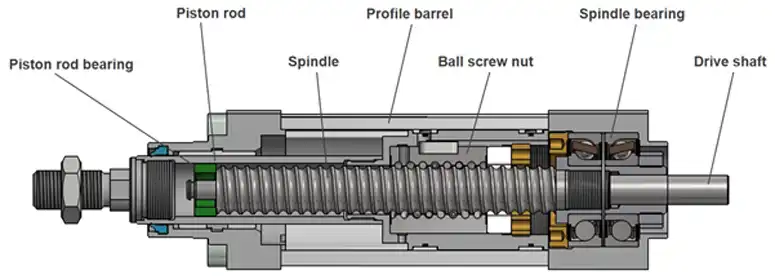
Torque is the twisting power produced by a motor. In an electric linear actuator, that rotational torque is converted into linear motion through mechanisms such as ball screws, lead screws or belt drives.
Force, sometimes called actuation force, is the pushing or pulling power at the actuator’s output. It’s what allows the actuator to lift, clamp, or move a load.
Speed refers to how fast the actuator’s rod extends or retracts. It’s typically measured in inches or millimeters per second and determines how quickly your application completes each stroke.
Because all three are linked through the motor and mechanical design, you can’t maximize torque, force, and speed at the same time. Increasing one usually means decreasing another.
Tip: If you’re unsure how torque, force, and speed translate to your application, our engineers can help. Request technical guidance for sizing and selection support.
Understanding the Trade-Offs
| High Force, Lower Speed | Applications that involve lifting heavy weights or applying strong clamping pressure need high actuation force. These actuators often use gear reduction or finer lead screws, which deliver greater thrust, but slower travel speeds. |
| High Speed, Lower Force | When quick positioning or frequent cycling is essential, speed takes priority. High speed electric linear actuators often use screws with high pitches or belt drives to reduce friction and move quickly. The trade-off is reduced available force. |
| Balanced Performance | Many industrial applications need a balance of both. Medium-speed, medium-force actuators are often ideal for automated systems where efficiency, precision, and reliability are all equally important. |
Need a versatile solution? Contact our team to discuss balanced actuators that handle both power and speed demands.
Practical Application Examples
- Heavy Load Lifting – A press or lift system may require 5,000 N of force at a slow speed. Choose a robust actuator with high torque capacity and strong gear reduction.
- Fast Sorting or Indexing – A conveyor diverter that cycles rapidly benefits from a lightweight, high-speed linear actuator with moderate force output.
- Precision Automation – For machine positioning or assembly equipment, look for balanced torque-to-speed ratios and feedback options to ensure repeatable accuracy.
Key Selection Steps
- Define Load and Travel – Determine the weight or resistance your actuator must overcome and how far it must move.
- Identify Required Speed – Decide how quickly the motion must complete each cycle.
- Evaluate Duty Cycle – Consider how often the actuator runs and whether cooling or rest periods are needed.
- Compare Performance Curves – Review the manufacturer’s torque, force, and speed charts to find where your needs intersect.
- Factor in Environment and Mounting – Conditions like vibration, temperature, and mounting orientation all affect performance and life.
- Select Control and Feedback Options – Position sensors, encoders, and limit switches to improve accuracy and safety.
Why It Matters
Selecting the right electric linear actuator isn’t about finding the model with the highest numbers. It’s about finding the one that best matches your system’s priorities. By understanding how torque, force, and speed interact, you’ll ensure better performance, longer actuator life, and more efficient automation.
Whether your project calls for a high-speed linear actuator for quick travel or a heavy-duty electric linear actuator for high thrust, knowing how torque, force, and speed relate will help you make a confident choice.
Accu Tech USA offers a full range of electric linear actuators and engineering support to help you size and select the ideal model for your application.
Contact our team to discuss your project or learn more about our high-performance motion control solutions.
